- Android v7 or higher, written in Kotlin v2.x or higher
- iOS v15.0 or higher, written in Swift
- Hybrid frameworks are not supported
To help you get started implementing the mobile SDK, you must purchase the basic implementation package from NiCE. A partner of NiCE leads you through the implementation.
You may also want to purchase Professional Services hours from NiCE for questions that setup outside of the Mobile SDK.
Mobile SDK lets you integrate CXone Mpower digital chat into your enterprise mobile phone apps. This lets app users chat with your contact center agents and bots through digital![]() Any channel, contact, or skill associated with Digital Experience. chat channels. The SDK simplifies the process of implementing digital chat; developers do not need to handle business logic implementation. The main task of your developers is visually displaying and managing features that you set up in CXone Mpower, like push notifications or rich messages
Any channel, contact, or skill associated with Digital Experience. chat channels. The SDK simplifies the process of implementing digital chat; developers do not need to handle business logic implementation. The main task of your developers is visually displaying and managing features that you set up in CXone Mpower, like push notifications or rich messages![]() Elements in digital messaging such as buttons, images, menus, and option pickers..
Elements in digital messaging such as buttons, images, menus, and option pickers..
The SDK supports both iOS and Android apps. iOS apps must be written in Swift ![]() and Android apps must be written in Kotlin
and Android apps must be written in Kotlin ![]() . Additionally, the SDK requires a minimum Android version of 7.0 and a minimum iOS version of 15.0.
. Additionally, the SDK requires a minimum Android version of 7.0 and a minimum iOS version of 15.0.
With Mobile SDK:
- You can implement both live chat and chat messaging channels. The SDK does not support chat through Guide.
- Live chat is real-time messaging.
- Chat messaging is asynchronous messaging, like direct messages (DMs).
- Contacts can have multiple interactions with your contact center at the same time through multi-thread
 In a multi-threaded app, contacts can create as many threads as they want to discuss new topics. These threads can be active at the same time. messaging. You can also set up a single-thread
In a multi-threaded app, contacts can create as many threads as they want to discuss new topics. These threads can be active at the same time. messaging. You can also set up a single-thread In a single-threaded app, each contact has one chat thread that handles any interaction they have with your organization. configuration.
In a single-threaded app, each contact has one chat thread that handles any interaction they have with your organization. configuration. - You can use rich media to add interactive messages like quick replies, lists, or links to your in-app chat.
- Contacts and agents can share attachments with each other, like videos and documents.
- Contacts and agents can stay engaged by seeing when the other is typing.
- You can trigger in-app and push notifications based on events, such as the arrival of a new message.
- You can create proactive rules to pop content in the app based on events or conditions.
- You can jump start interactions with welcome messages and pre-chat forms to gather initial information from a contact.
- You can set up inactivity popups that warn contacts when the chat will expire due to inactivity.
- You can allow contacts to request their conversation transcript.
For an at-a-glance look at the benefits of the SDK, you can check out the Mobile SDK data sheet ![]() . You can also watch a short demo video
. You can also watch a short demo video ![]() .
.
A software development kit (SDK) is like a toolbox for developers. It provides a set of tools and resources that make building software applications easier. You could think of it as a collection of pre-made building blocks. These building blocks have existing functionality. Your developers can use these existing blocks instead of building the functionality on their own from the ground up. The following are four general benefits to using an SDK:
-
Efficiency: The SDK provides ready-made tools and pre-built components that save developers time. Instead of reinventing the wheel, they can focus on the unique aspects of their app.
-
Consistency: The SDK ensures consistency across different apps. By using the same set of tools and libraries, developers maintain a uniform experience for users.
-
Platform Compatibility: The iOS and Android SDKs are tailored for their respective platforms. They handle platform-specific complexities, making it easier to create cross-platform apps.
-
Quality Assurance: With the logger, developers can verify their code, catch bugs early, and deliver more reliable software.
In summary, an SDK simplifies development, ensures quality, and fosters collaboration, making it an essential tool for efficient app creation.
SDK Resources
Download the SDK packages from public GitHub repositories (Android ![]() iOS
iOS ![]() ). Both repos contain a README file to help you get started developing. They also offer use cases with code samples in /docs. Use these as inspiration as you develop your chat. Both repositories also include changelogs.
). Both repos contain a README file to help you get started developing. They also offer use cases with code samples in /docs. Use these as inspiration as you develop your chat. Both repositories also include changelogs.
You can access the API references in your browser (Android ![]() iOS
iOS ![]() ).
).
Your developers can also look at sample applications for both Android ![]() and iOS
and iOS ![]() platforms. These help developers see examples of implemented functionality.
platforms. These help developers see examples of implemented functionality.
Mobile SDK Versioning
The SDK versions generally update along with the CXone Mpower major marketing releases, like 25.4, 26.1, and so forth. In GitHub, each release version is tagged according to the semantic versioning explained below.
You are responsible for keeping your app up to date as the SDK also updates. The SDK Resources section above provides links to the most up-to-date resources. In the SDK repositories, you can use the tags to find previous versions of the SDK. Also, the sdkVersionNotSupported error lets you know that your SDK version is outdated and you should update it.
Be aware that the SDK is backward compatible through the last two major versions.
NiCE supports the current and one previous major version of the SDK. For example, if the current version is 2.2, NiCE supports v2.2 and 1.3 (the latest 1.x.x version).
Version Changes
When the SDK version changes from release to release, the version number denotes the type of change:
-
2.0.0: The first number denotes the major API change.
-
2.1.0: The second number denotes a non-breaking change. Often, new features are added as non-breaking changes.
-
2.0.1: The third number denotes a bug fix. These are always backwards compatible.
Bug Fixes
NiCE Professional Services works with you on bug fixes. You can submit bugs through them (or the implementation partner), and they communicate fixes to you in addition to the SDK changelog.
Also, any bugs are fixed in the currently-supported versions. For example, if the current version is 3.0, then the two supported versions are 3.0 and 2.3 (the latest version from 2.x). If you found a bug in v2.1, NiCE would fix it for 2.3 and 3.0, but not 2.1 or 2.2.
How the Mobile SDK Fits into Digital Experience
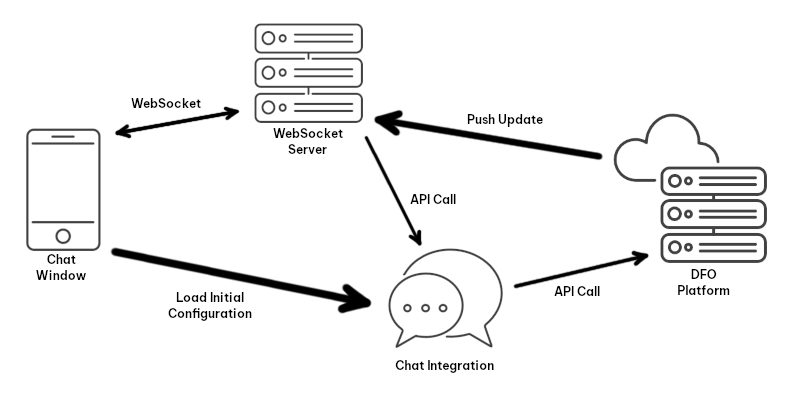
The Mobile SDK is a way to extend Digital Experience and provide digital chat in mobile apps. Digital Experience is the part of CXone Mpower that supports digital channels. Examples of digital channels are WhatsApp, posts on Facebook, or digital chat. To add CXone Mpower digital chat into your apps, you must configure certain features in the Digital Experience section of the CXone Mpower interface. Then, with the SDK, you access and use features that you set up in CXone Mpower.
For example, part of the getting started process is to set up a digital chat channel in CXone Mpower. Then, your app must create a WebSocket connection with the digital chat channel that you created. You could also set up advanced features like welcomes messages or pre-chat surveys. These give you a variety of options to streamline your app users' experience. Users can provide initial information about their issue or request, enter basic personal data, and so forth. These features are initially set up in CXone Mpower, which you can then use with the SDK.
Chat UI
The Mobile SDK comes with a default UI/UX module. You can choose to implement it as part of the standard implementation package. This substantially reduces the implementation time.
Default UI Module
The default module automatically handles all chat features, which reduces the need for any further development on your part, such as:
-
Rich messages
 Elements in digital messaging such as buttons, images, menus, and option pickers.
Elements in digital messaging such as buttons, images, menus, and option pickers.
-
Attachments
-
Working with files
-
Error messages
-
Emoji behavior
The Mobile SDK sample application showcases the default UI/UX. Documentation for the UI/UX module is in the module, itself, for your developers to review.
Color Customization
You can choose the colors of 33 different parts of the chat UI, ranging from headings to buttons. This includes both light mode and dark mode. As part of the standard implementation package, you define these colors. The default colors follow NiCE branding, which you can change.
After implementation, your developers can control colors with a color manager in the ChatStyle class.
Develop Your Own UI
You can also choose to use or develop your own UI; you are not obligated to use the default UI/UX. If you use your own UI (or a third-party UI package), NiCE does not provide support for it.
Similarly, you may want to make certain configurations customizations to the default UI, like localization, push notifications, and OAuth authentication. If you want to support any language aside from English, you must supply translations for the text strings. If you implement a non-English language, be sure to test all areas of the UI to ensure the display is handled appropriately.
If your developers make additional customizations on top of the standard UI/UX, NiCE does not provide support for those changes.
Mobile SDK Limitations
-
To help you get started implementing the Mobile SDK, you must purchase the basic implementation package from NiCE. A partner of NiCE leads you through the implementation.
-
You may want to purchase Professional Services hours from NiCE for questions about setup outside of the Mobile SDK.
-
The SDK cannot be used without an existing mobile app. You must have your own application written natively in Kotlin or Swift.
-
Non-native or hybrid frameworks are not supported, such as React Native.
-
This SDK works with standalone Digital chat, not chat via Guide.
Before You Start Developing
Consider the following items before building with the mobile SDK:
- Do you have both an administrator and agent account in CXone Mpower? Can an administrator assist you in setting up the necessary features in the CXone Mpower platform?
- Is your mobile app available for iOS (Apple), Android, or both? Are your developers familiar with the Swift and Kotlin languages?
- Do you have existing chat messaging channels, or do you want to create a new one?
- Will you use OAuth to authenticate your app users? If yes, which OAuth provider will you use?
- Do you want to offer single- or multi-threaded conversations?
- Will you use proactive actions like pop-ups or welcome messages?
- Do you want to use push notifications? Do you have existing Firebase or Apple Developer accounts?
- Which types of rich messages do you want to set up? What are some use cases where you can leverage these interactive messages?
- Do you want to track user data? How can you use the visitor events to produce analytics?
Key Terms
| Term | Details |
|---|---|
| Thread | A conversation within the chat app. The first message sent by either the agent or contact |
| Single-Thread | An app design where the contact can only have one conversation at a time. |
| Multi-Thread | An app design where the contact can have multiple conversations at a time. |
| Channel | In the context of Digital Experience, channel refers to the type of messaging or the platform used for communication. For example, you could have a WhatsApp real-time messaging channel. The mobile SDK lets you add a chat messaging channel to your mobile app. A channel is created in the CXone Mpower platform. This determines the settings of the channel along with a channel ID. You use this ID to initiate the chat channel when an app user opens the chat. |
| ChannelId | The ID of the digital chat channel created in the Digital section of CXone Mpower. You can find this in the chat channel's settings in CXone Mpower (ACD > Digital > Points of Contact Digital > Chat > Initialization & Test). |
| BrandId | This is like a tenant |
| CustomerId | The unique ID of the chat end user. The SDK creates this ID when the chat is initialized. If you have OAuth set up, this ID stays the same for each contact across all their devices. If you do not have OAuth set up, this ID is different for each device; the ID becomes like a guest login. |
| Region or Environment | The location in the world where your CXone Mpower deployment is hosted. This can be: Australia (AU1), Canada (CA1), Europe (EU1), Japan (JP1), North America (NA1), or United Kingdom (UK1). The developer must use the same region where your CXone Mpower system is hosted, otherwise the chat connection is rejected. |
| Contact, Customer, and User | These terms all refer to the end-user of the mobile app. The online help typically uses the term contact. In the SDK documentation and code comments, you are likely to see customer and user. |
| CXone Mpower | The core platform where you manage and access all the customer experience tools that CXone Mpower offers. Depending on which chat features you want to offer in your mobile app, an administrator with the necessary user account permissions must complete several setup tasks in CXone Mpower. |
| Digital Experience | The section of CXone Mpower where you can manage everything about digital channels. |

