Cloud TTS Hub supports the use of Speech Synthesis Markup Language (SSML). SSML is an XML-based markup language that lets you control how text is synthesized into speech. You can use it to fine-tune pronunciation, rate of speech, voice pitch, volume, and more.
SSML provides a standard markup language, but providers may implement it differently. You need to use the supported markup from the TTS provider in your TTS scripts. Other TTS markup may not work. Refer to the documentation from your TTS service provider:
To use SSML in Studio scripts, text input must be:
- Valid XML.
- Valid SSML.
- Contained within <speak> </speak> tags.
- Marked up with one attribute per tag (this includes the <speak> tag). Attributes in SSML allow you to specify how the text is read, such as being read as a number or with a specific voice.
- Assigned to a dynamic data object or a variable in a SNIPPET action in your script. The object or variable you assign the marked up text to must be used later in your script in the appropriate place to be passed to the TTS service provider. See the examples later in this section. When working with SSML in snippets:
- You can assign SSML text to dynamic data object or regular variables.
- You can assign a message as a single block of text to a variable, or you can break it up across multiple variables.
The SSML assigned to a variable must contain fewer that 300 characters. If the text is longer than this, you can use assign it to multiple variables or properties of a dynamic data object.
Use the variable you assign the SSML to in the Sequence property of the PLAY action in your script. You can learn more about working with TTS prompt sequences in Studio.
- Remove XML namespace parameters from the SSML tags when you add them to your snippets. For example, parameters such as xmlns="http:/http://w3.org/2001/10/synthesis" must be removed.
Double quotes that appear within the XML must be removed in the snippet's variable or dynamic data object assignments. For example, format XML in your snippet variable assignments like this: <ASSIGN playSSML = "<speak xml:lang=en-US><voice name=en-US-JennyNeural> Good morning Chris! </voice></speak>". This is the original XML used in the example:
<speak xml:lang="en-US"> <voice name="en-US-JennyNeural"> Good morning Chris! </voice> </speak>
You can add the following actions to any script where you need TTS with SSML. When you do, it should follow this example:
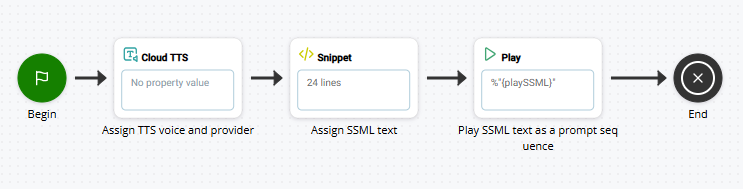
In the example, the CLOUD TTS action defines the Cloud TTS Hub TTS provider and voice. The SNIPPET action contains the marked up SSML text. It can be located before or after CLOUD TTS, but must come before PLAY. The SSML is assigned to a variable that's passed to the PLAY action as a prompt sequence. For virtual agent![]() A software application that handles customer interactions in place of a live human agent. scripts, use a VOICEBOT EXCHANGE action instead of PLAY.
A software application that handles customer interactions in place of a live human agent. scripts, use a VOICEBOT EXCHANGE action instead of PLAY.
Example of One Attribute Per Tag in SSML
This example shows SSML markup with one attribute per tag. The original XML is:
<speak xml:lang="en-US">
<voice name="en-US-JennyNeural"> Good morning Chris! </voice>
<voice name="en-US-ChristopherNeural"> Good morning to you too, Jenny! </voice>
</speak>
To use this example in a SNIPPET action in your script, assign it to a variable and remove the double quotes:
ASSIGN playSSML = "<speak xml:lang=en-US><voice name=en-US-JennyNeural>Good morning Chris!</voice>
<voice name=en-US-ChristopherNeural>Good morning to you too, Jenny!</voice></speak>"Example of Multiple Sentences with Different Markups in SSML
This example shows multiple sentences between the
<speak xml:lang="en-US">Here are <say-as interpret-as="characters">SSML</say-as> samples. I can pause <break time="3s"/>.I can say cardinal numbers like <say-as interpret-as="cardinal">1135</say-as>. I can say numbers as digits like <say-as interpret-as="characters">1135</say-as>.</speak>This is the variable assignment you would use in your SNIPPET action:
ASSIGN playSSML = "<speak xml:lang=en-US>Here are <say-as interpret-as=characters>SSML</say-as> samples. I can pause <break time=3s/>. I can say cardinal numbers like <say-as interpret-as=cardinal>1135</say-as> I can say numbers as digits like <say-as interpret-as=characters>1135</say-as>. </speak>"Example of a Dynamic Data Object with Marked Up Text in Snippet Code
This example shows assigning marked-up text to a dynamic data object:
DYNAMIC promptSSML
ASSIGN promptSSML.prompt[1].textToSpeech = "<speak>The SSML should be read in the TTS voice selected in the CLOUD TTS action.\<speak\>";
ASSIGN promptSSMLJSON = "{promptSSML.asjson()}";Example of One Message Spread Across Multiple Variables in SNIPPET Code
This example shows using multiple variables for text that's longer than 300 characters.
The value of myText2 includes the text of myText. The text of
ASSIGN myTime = "2:30pm"
ASSIGN myText = "<speak> Here are some examples of what CXone Mpower can do with SSML and cloud TTS. CXone can include a break <break time=3s/> in a spoken sentence as well as read back numbers in different ways."
ASSIGN myText2 = "{myText} For example, saying the number <say-as interpret-as=verbatim>12345</say-as> as individual digits or reading it as a cardinal number like this. <say-as interpret-as=cardinal>12345</say-as> ."
ASSIGN myText3 = "{myText2} CXone can also read back words as words or as individual characters <say-as interpret-as=characters>like this</say-as> ."
ASSIGN myText4 = "{myText3} CXone can also use SSML to slow down spoken sentences. <prosody rate=70%> to help people better understand something that's being said </prosody> "
ASSIGN myText5 = "{myText4} or speed them up <prosody rate=170%> where, for example, the fine print of an agreement can be read back in a short amount of time. </prosody> "
ASSIGN myText6 = "{myText5} Combining SSML and cloud TTS, CXone can also be used for many other things, like reading back time correctly like this. Currently, it's<say-as interpret-as=time format=hms24 detail=2>{myTime}</say-as></speak>"To have the entire text read as a prompt, use the variable that holds all the text in the Sequence property of the PLAY action. Following the preceding example, you would use configure Sequence with "%{myText6}". You can learn more about working with TTS prompt sequences in Studio.

