There are two types of fallback. NLU and action fallback are for when your bot doesn't understand what the contact means or isn't sure what to do next. A third type of fallback is for rich messages, and is used when the channel doesn't support the rich content being sent.
| Concept | Definition | Example | What the Bot Does |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Utterance |
Anything a contact |
"I lost my password." "What is my balance?" "Are you a bot?" |
The bot uses Natural Language Understanding (NLU) to analyze each contact utterance to determine its meaning, or intent. |
|
Intent |
What the contact wants to communicate or accomplish. Every message the contact sends has an intent. |
"I lost my password" has the intent of "reset password". "Hello" has the intent of "greeting". |
The bot analyzes a contact's message using NLU |
|
Entity |
A defined piece of information in a contact's message. | Person or product name, phone number, account number, location, and so on. | The bot uses NLU to identify entities in a contact's message. Entities help the bot understand what the contact's message means. |
|
Slot |
An entity extracted from a contact's message and saved for use in bot responses. Similar to a variable. | Creating a slot for contact name lets the bot use that name in responses during an interaction, making it more personal. | When configured to do so, the bot extracts an entity from a contact message and saves it in a slot. You can have your bot use this information later in the conversation. |
|
Rule |
Defines bot responses to messages that don't change meaning with context. |
|
Rules are one of two ways you can configure how your bot responds to an intent. Rules are useful for certain kinds of intents, but not all intents. |
|
Story |
Trains a bot to handle an interaction based on message intent and conversational context. | In an interaction about a forgotten password, the bot would respond to "How do I do that?" in one way. If the interaction were about creating a new account, the response would be quite different even though in both cases the contact is using the same words with the same intent—to get more information. | Stories are the second of two ways you can configure how your bot responds to an intent. Stories teach the bot how to use the context of the conversation to respond appropriately. |
|
Bot Action |
Anything a bot says or does while handling an interaction. |
In an interaction about a forgotten password, the bot responds by sending the link to the password reset FAQ on the website. When a contact expresses frustration, such as "I don't understand! It's not working!!!" the bot responds with "I'm sorry. Would you like me to transfer you to a human agent?" When the contact says yes, the bot initiates the transfer. |
Bot actions are the options you have when defining how you want your bot to respond to each intent. They give you the flexibility to configure each response to achieve the outcome that meets the contact's needs. |
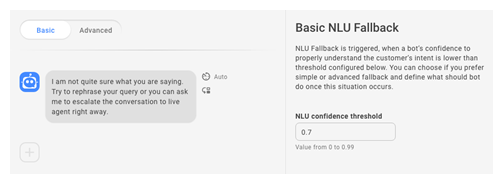
Configure NLU Fallback
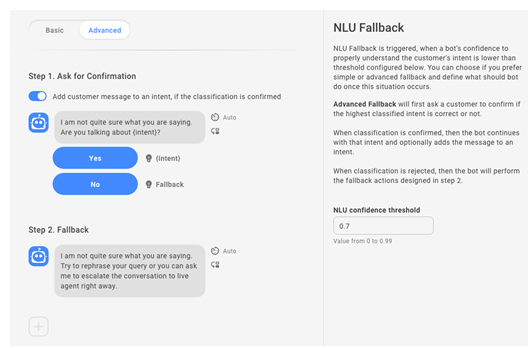
NLU fallback is triggered when a bot's confidence to properly understand the customer's intent is lower than the NLU confidence threshold![]() Measures the confidence in a bot's intent prediction. Confidence below threshold triggers fallback.. You can choose basic or advanced fallback and design what the bot should do. Advanced fallback will ask the customer to confirm the intent. If the intent is confirmed, the conversation continues. If not, the bot moves on to the fallback message.
Measures the confidence in a bot's intent prediction. Confidence below threshold triggers fallback.. You can choose basic or advanced fallback and design what the bot should do. Advanced fallback will ask the customer to confirm the intent. If the intent is confirmed, the conversation continues. If not, the bot moves on to the fallback message.
- In CXone Mpower, click the app selector
 and select Bot Builder.
and select Bot Builder. - Click the bot you want to work with.
- Click Dialogues
 in the left icon menu.
in the left icon menu. - On the Fallback tab, click NLU.
- Click the toggle to select either Basic or Advanced.
- If you selected Basic fallback:
- To use a custom value for NLU confidence threshold, enter that value in the field. This sets the minimum confidence level the bot must have to predict an intent based on a contact's utterance
 What a contact says or types..
What a contact says or types.. - Click the message to edit the default response.
- If you want your bot to use the handover
 The transfer of a contact from a virtual agent to a live agent. rule if it still doesn't understand, click the plus sign + and select Handover.
The transfer of a contact from a virtual agent to a live agent. rule if it still doesn't understand, click the plus sign + and select Handover.
- To use a custom value for NLU confidence threshold, enter that value in the field. This sets the minimum confidence level the bot must have to predict an intent based on a contact's utterance
- If you selected Advanced fallback:
- Under Step 1, if the toggle is turned on and the customer confirms the intent, the message is added to the intent. Click the message to edit the default response. You can also change the text and intents of the buttons.
- Under Step 2, click the message to edit the default response.
- If you want your bot to use the handover
 The transfer of a contact from a virtual agent to a live agent. action if it still doesn't understand, click the plus sign + and select Handover.
The transfer of a contact from a virtual agent to a live agent. action if it still doesn't understand, click the plus sign + and select Handover.
- When you're finished making changes, click Train and Stage to update your bot model
 Version of a bot that has been trained and staged to test this change.
Version of a bot that has been trained and staged to test this change.
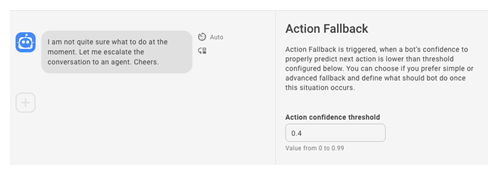
Configure Action Fallback
Action fallback is triggered when a bot's confidence to properly react to the message lower than the confidence threshold![]() Measures how confident a bot is about the next action it should take. The default level is 40% (0.4), so fallback is triggered at any level below that.. It defines what the bot should do when it's not sure what action to take.
Measures how confident a bot is about the next action it should take. The default level is 40% (0.4), so fallback is triggered at any level below that.. It defines what the bot should do when it's not sure what action to take.
- In CXone Mpower, click the app selector
 and select Bot Builder.
and select Bot Builder. - Click the bot you want to work with.
- Click Dialogues
 in the left icon menu.
in the left icon menu. - On the Fallback tab, click Action.
- To use a custom value for Action confidence threshold, enter that value in the field.
- Click the message to edit the default response.
- If you want the bot to use the handover
 The transfer of a contact from a virtual agent to a live agent. rule if it still doesn't understand, click the + icon and select Handover.
The transfer of a contact from a virtual agent to a live agent. rule if it still doesn't understand, click the + icon and select Handover. - When you're finished making changes, click Train and Stage to update your bot model
 Version of a bot that has been trained and staged to test this change.
Version of a bot that has been trained and staged to test this change.